
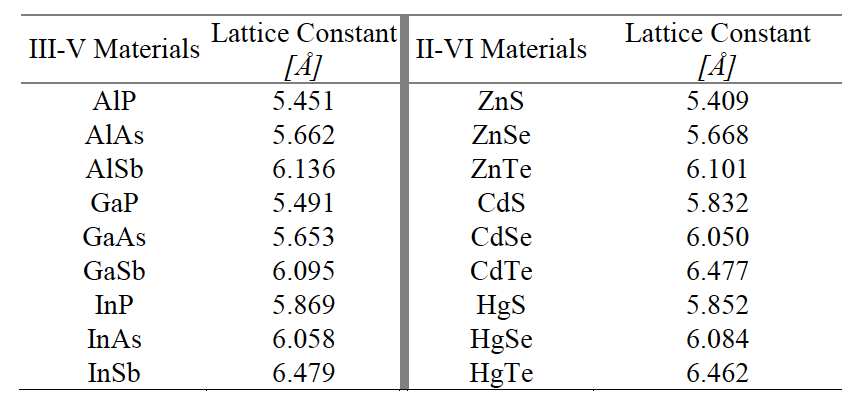
Using modern software such as Olex2, one can solve a crystal structure from crystallographic output files. Crystallographic information can be collected via x-ray diffraction, providing information on the locations of electron density within a crystal structure. Calcium fluoride is a classic example of a crystal with a fluorite structure. These relationships can help predict the behavior of crystalline materials, as well as introduce the ability to tune their properties. It is important to understand the crystal structure of materials to form structure-property relationships. Experimental data from Straumanis Cu-In alloys, density, lattice parameters, thermal expansion (23.52Kb) Spectroscopically pure Cu has a lattice parameter a25 3.61491 (corrected for refraction), and a thermal expansion coefficient alpha 14.87 × 10-6C-1 between 15 and 55C. So after finding out d-spacing from detected Bragg’s angle, we can figure out the lattice parameter which contains vital structural information. Lattice constants for fluorite and antifluorite materials at 300 K MaterialĬrystallography is a powerful tool to investigate the structures of crystalline materials. What is the formula to calculating the lattice parameter or lattice constant of Orthorhombic structure Theres an orthorhombic phase of Cu5FeS4 in the XRDs of one sample. D-spacing, which is the inter plane distance d in Bragg’s equation, is decided by the lattice parameter a, b, c, as shown below. It is one of the most common structures for metals. In terms of lattice parameter (a)it is equal to, a 2R(sqrt(2)). The antifluorite structure of magnesium silicide Mg 2Si. The Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) unit cell can be imagined as a cube with an atom on each corner, and an atom on each face. The lattice parameters are the quantities specifying a unit cell or the unit of the periodicity of the atomic arrangement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
